Entra ID Security 2026: Defend Against Emerging Threats in the Age of Identity Warfare
Entra ID Security 2026 is no longer about reacting to known threats. It is about anticipating adversaries who operate faster than human response, abuse artificial intelligence, exploit cloud-native trust boundaries, and weaponize identity itself.
Modern cyberattacks no longer begin with malware. They begin with identity compromise. In a world dominated by SaaS, remote work, APIs, and automation, Microsoft Entra ID security has become the final control plane protecting enterprises from catastrophic breaches.
By 2026, organizations that treat Entra ID as “just another directory” will fail. Those who architect identity as a resilient, zero-trust security system will survive.
The Urgency of Entra ID Security in 2026
Imagine a breach that does not exploit software vulnerabilities, does not deploy ransomware, and does not trigger antivirus alerts. Instead, it silently manipulates authentication tokens, elevates privileges using misconfigured roles, and persists indefinitely without detection.
This is not science fiction. This is the direction of identity-based attacks targeting Entra ID Security 2026.
Why Today’s Entra ID Security Is Not Enough
- Traditional perimeter security has collapsed
- Identity is accessible from anywhere on the internet
- Attackers target misconfigurations, not exploits
- AI enables faster credential harvesting and phishing
- Cloud trust models are abused at scale
Security teams still focus on endpoint protection while attackers focus on identity dominance. Once Entra ID is compromised, attackers gain access to:
- Microsoft 365 data (Exchange, SharePoint, Teams)
- Azure subscriptions and workloads
- SaaS platforms via Single Sign-On
- Privileged administrative control
- Token-based persistent access
That is why Entra ID Security 2026 must be treated as a **strategic defense system**, not a configuration checklist.
The Looming Shadow: Entra ID in 2026
Beyond Today’s Headlines
Most Entra ID security guidance today focuses on:
- Enable MFA
- Use Conditional Access
- Review sign-in logs
These controls are necessary — but insufficient for 2026.
Future attackers will not brute-force passwords. They will:
- Abuse OAuth consent frameworks
- Exploit service principals and managed identities
- Leverage AI-generated phishing at scale
- Persist using refresh token theft
- Manipulate hybrid trust relationships
This means Entra ID Security 2026 must evolve from static controls into **adaptive identity defense**.
Anticipating the Adversary
Attackers in 2026 will be:
- Cloud-native
- API-driven
- AI-assisted
- Patient and persistent
They will not “hack in.” They will authenticate.
According to Microsoft threat intelligence, over 80% of breaches already involve identity compromise. By 2026, that number will be higher.
Organizations that fail to harden Entra ID identity security will not detect breaches until damage is irreversible.
What Is Truly at Risk?
If Entra ID defenses fail, organizations lose:
- Control over user access
- Trust in authentication signals
- Visibility into lateral movement
- Ability to contain incidents
- Regulatory compliance
In identity-centric breaches, attackers do not need to move laterally — they already have legitimate access.
This is why Entra ID Security 2026 must prioritize:
- Prevention over detection
- Adaptive risk over static rules
- Least privilege by default
- Continuous verification
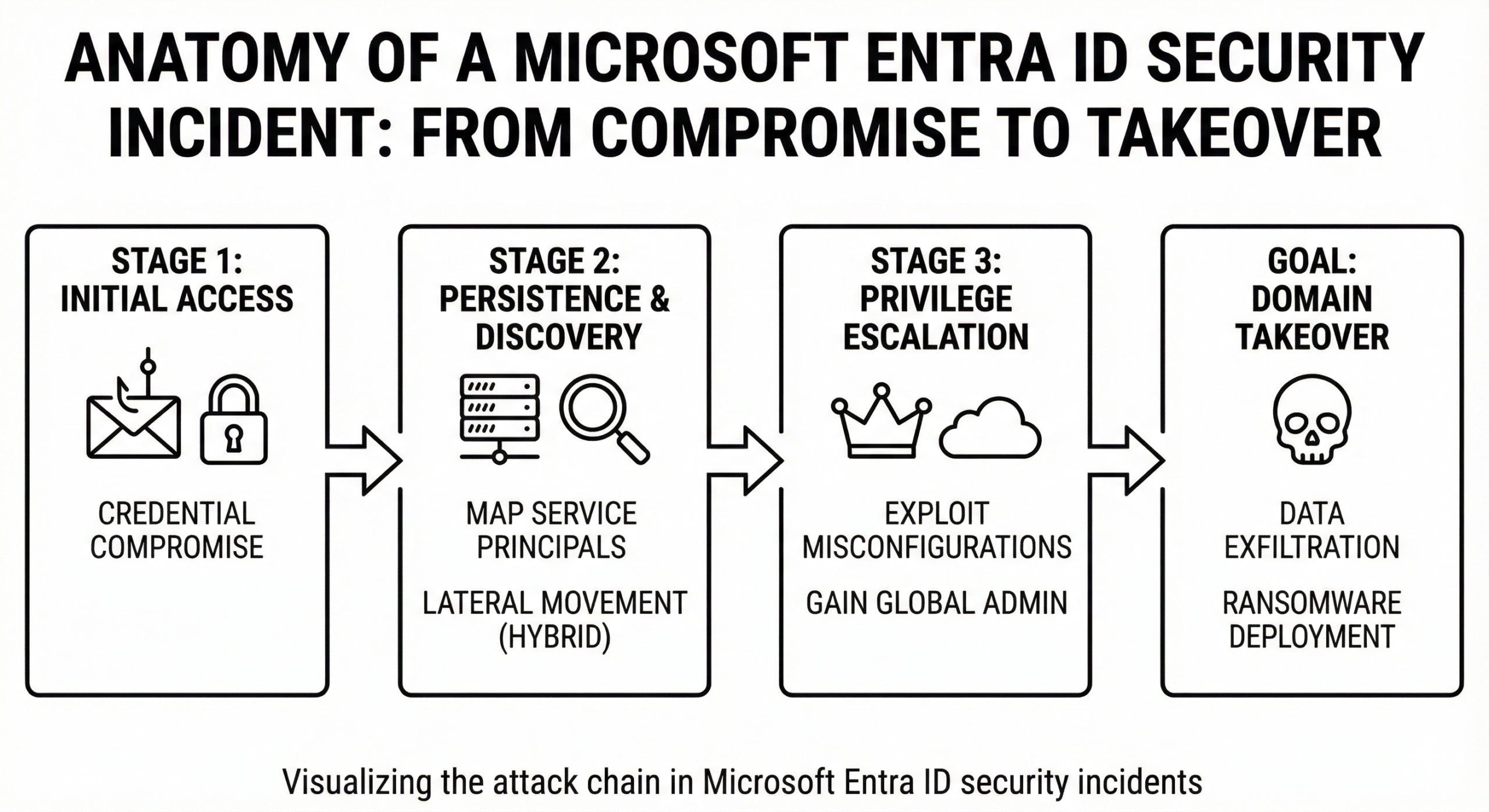
Reverse-Engineering Future Entra ID Exploits
Hypothetical 2026 Attack Chain
Let’s walk through a realistic future attack scenario targeting Entra ID:
- Attacker compromises a third-party SaaS vendor
- OAuth application gains excessive permissions
- Tokens are silently issued without MFA
- Refresh tokens persist for months
- Privileged roles are activated using PIM abuse
- Logs appear normal due to legitimate authentication
No malware. No alerts. No brute force.
This is the future threat model driving Entra ID Security 2026.
Persistence Techniques of Tomorrow
- Service principal backdoors
- Hidden API permissions
- Token replay attacks
- Conditional Access bypass via trusted locations
- Hybrid identity trust abuse
Traditional SOC tooling struggles to detect these techniques because they look like normal identity behavior.
PowerShell: Detecting Suspicious OAuth Applications
Proactive defense begins with visibility. The following PowerShell example helps identify applications with excessive permissions:
Get-MgApplication | ForEach-Object {
$app = $_
Get-MgApplicationAppRoleAssignment -ApplicationId $app.Id |
Where-Object {$_.PrincipalType -eq "ServicePrincipal"} |
Select-Object @{Name="AppName";Expression={$app.DisplayName}},
ResourceDisplayName,
AppRoleId
}
This script supports proactive audits aligned with Entra ID Security 2026 principles.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is Entra ID really the primary attack surface?
Yes. Identity is now the most targeted attack vector in cloud environments. Protecting Entra ID is protecting the enterprise.
Is MFA enough for Entra ID Security 2026?
No. MFA is foundational, but attackers increasingly bypass weak MFA implementations. Phishing-resistant MFA is mandatory.
Should organizations abandon hybrid identity?
Not immediately. However, hybrid identity significantly expands the attack surface and must be tightly governed.
Key Takeaways
- Entra ID Security 2026 requires forward-looking defense
- Attackers will authenticate, not exploit
- Identity governance is as critical as MFA
- Reactive security models will fail
Next Part: Proactive Defense Strategies for Entra ID Security 2026 — Zero Trust evolution, adaptive Conditional Access, and AI-driven identity protection.
Proactive Defense Strategies for Entra ID Security 2026
Entra ID Security 2026 demands a fundamental shift in mindset. The era of reactive identity defense is over. Waiting for alerts, reviewing logs after incidents, or applying controls only after breaches is no longer sufficient.
In 2026, organizations must assume compromise and design identity systems that are resilient, adaptive, and self-correcting. This section explores how to move from reactive security to proactive identity defense.
From Reactive Patching to Proactive Identity Posture
Traditional security focuses on patching vulnerabilities after discovery. Identity attacks, however, exploit:
- Misconfigurations
- Excessive permissions
- Implicit trust
- Human behavior
These are not patched — they are architected.
To secure Entra ID Security 2026, organizations must continuously evaluate identity posture, not just compliance.
Key Principles of Proactive Entra ID Defense
- Assume breach at all times
- Continuously verify identity risk
- Automate least privilege enforcement
- Eliminate standing access
- Design for identity failure scenarios
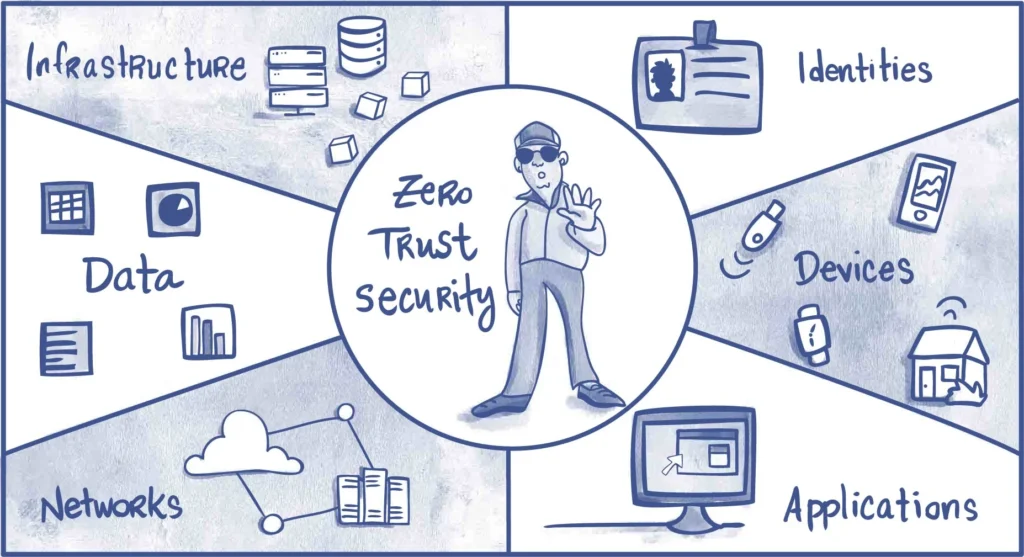
Microsoft’s Zero Trust framework strongly aligns with these principles. However, Zero Trust must evolve to meet future threats.
Zero Trust Evolution for Entra ID Security 2026
Zero Trust is often misunderstood as “MFA everywhere.” In reality, Zero Trust is an adaptive trust model that continuously evaluates:
- User risk
- Device health
- Location anomalies
- Behavior patterns
- Session context
By 2026, static Conditional Access policies will fail. Attackers will simulate compliant conditions.
Next-Generation Zero Trust Identity Model
- Risk-based authentication, not rule-based
- Continuous access evaluation (CAE)
- AI-driven anomaly detection
- Session-level enforcement
This is the future of Entra ID Security 2026.
Conditional Access Reimagined
Conditional Access (CA) is the most powerful security control in Entra ID — and the most misconfigured.
In 2026, effective Conditional Access must:
- Deny by default
- Adapt dynamically to risk
- Protect tokens, not just sign-ins
- Apply to service principals and workloads
Common Conditional Access Failures
- Excluding legacy protocols
- Trusted location abuse
- Overuse of “report-only” mode
- Ignoring workload identities
For deeper Conditional Access strategies, refer to internal guidance at Conditional Access best practices.
Identity Governance Reimagined
Identity governance is the most overlooked pillar of Entra ID security.
By 2026, attackers will exploit:
- Orphaned accounts
- Unused privileged roles
- Long-lived service principals
- Stale group memberships
Automated Least Privilege
Manual access reviews are not scalable. Entra ID Security 2026 requires:
- Automated access expiration
- Just-In-Time (JIT) privileges
- Approval-based role activation
- Continuous entitlement evaluation
Privileged Identity Management (PIM) becomes mandatory, not optional.
PowerShell: Detecting Stale Privileged Assignments
Get-MgRoleManagementDirectoryRoleAssignment |
Where-Object {$_.AssignmentState -eq "Active"} |
Select-Object PrincipalId, RoleDefinitionId, StartDateTime
This script helps identify standing access that violates Entra ID Security 2026 principles.
Threat Hunting in Entra ID
Traditional SIEM tools focus on endpoints and networks. Identity threat hunting requires:
- Behavioral baselines
- Token anomaly detection
- OAuth abuse identification
- Impossible travel correlation
Microsoft Entra ID Identity Protection provides a starting point, but advanced organizations must go further.
Threat hunting becomes continuous, automated, and AI-assisted.
Graph API: Hunting Risky Sign-ins
Invoke-MgGraphRequest -Method GET ` -Uri "https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/identityProtection/riskySignIns"
This API enables proactive detection aligned with Entra ID Security 2026.
FAQs – Proactive Entra ID Defense
Is Conditional Access enough?
No. Conditional Access must be combined with governance, monitoring, and automation.
Can AI really detect identity threats?
Yes. Behavioral analytics is essential to detect token-based and consent-based attacks.
Should service principals be governed?
Absolutely. Service principals are one of the top attack vectors in cloud identity.
Key Points – Part 2
- Reactive identity security will fail by 2026
- Zero Trust must become adaptive
- Identity governance is critical
- Threat hunting must include identity signals
Next Part: Architecting Resilient Identity Infrastructure for Entra ID Security 2026
Architecting Resilient Identity Infrastructure for Entra ID Security 2026
Entra ID Security 2026 is not about preventing every breach. That is an unrealistic goal. Instead, it is about designing identity infrastructure that continues to function securely even when parts of it fail.
In modern cloud environments, identity must be treated as critical infrastructure — similar to power grids or financial systems. Resilience, isolation, and recovery are as important as prevention.
Designing for Failure: Assume Identity Will Be Targeted
Most organizations design Entra ID with the assumption that:
- Admins will never be compromised
- MFA will never be bypassed
- Tokens will never be stolen
By 2026, these assumptions will be dangerously wrong.
Entra ID Security 2026 requires designing for failure:
- What happens if a Global Admin is compromised?
- What happens if OAuth tokens leak?
- What happens if Conditional Access is misconfigured?
If the answer is “total compromise,” the architecture has failed.
Identity Micro-Segmentation
Network micro-segmentation is well understood. Identity micro-segmentation is not — yet.
Identity micro-segmentation means:
- Separating administrative identities
- Isolating workload identities
- Restricting blast radius of credentials
- Minimizing cross-tenant trust
In Entra ID Security 2026, a single identity should never provide access to:
- All administrative roles
- All subscriptions
- All SaaS applications
Best Practices
- Use dedicated admin accounts
- Separate break-glass identities
- Isolate CI/CD identities
- Apply Conditional Access per identity tier
For identity segmentation strategies, see internal guidance at Entra ID security architecture.
The Unhackable Account: MFA Evolution
By 2026, basic MFA will be insufficient.
Attackers already bypass MFA using:
- Token replay attacks
- Consent phishing
- MFA fatigue attacks
- Session hijacking
Entra ID Security 2026 requires phishing-resistant authentication.
MFA Controls That Matter in 2026
- FIDO2 security keys
- Certificate-based authentication
- Passkeys
- Passwordless sign-in
Passwords must be treated as legacy credentials.
Passwordless Nirvana
Passwordless authentication eliminates the most abused attack vector.
Benefits:
- No password to phish
- No password reuse
- No brute-force attacks
By 2026, organizations that still rely on passwords will experience disproportionate breach rates.
Microsoft documentation on passwordless authentication: Microsoft Passwordless Authentication
Disaster Recovery for Entra ID
Most organizations have disaster recovery plans for servers and data. Very few have disaster recovery plans for identity.
This is a critical failure.
Identity Disaster Scenarios
- Global Admin lockout
- Conditional Access misconfiguration
- Tenant-wide compromise
- Accidental mass deletion
Entra ID Security 2026 mandates identity recovery planning.
Mandatory Controls
- Break-glass accounts (offline MFA)
- Emergency access monitoring
- Role assignment backups
- Configuration change auditing
PowerShell: Audit Break-Glass Accounts
Get-MgUser | Where-Object {
$_.DisplayName -like "*break*"
} | Select DisplayName, AccountEnabled
Break-glass accounts must be monitored continuously as part of Entra ID Security 2026.
Resilience Through Automation
Manual identity management does not scale.
Automation ensures:
- Consistent enforcement
- Rapid remediation
- Reduced human error
Automation should cover:
- Role assignment expiration
- Conditional Access drift detection
- Stale account cleanup
- OAuth permission audits
Graph API: Detect Risky OAuth Grants
Invoke-MgGraphRequest -Method GET ` -Uri "https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/oauth2PermissionGrants"
This API is critical for identifying silent persistence mechanisms.
FAQs – Identity Resilience
Is passwordless mandatory by 2026?
For privileged identities, yes. Password-based admin access is no longer defensible.
How many break-glass accounts should exist?
At least two, stored securely, monitored continuously.
Does automation increase risk?
No. Poorly governed automation increases risk. Proper automation reduces it.
Key Points – Part 3
- Design identity assuming compromise
- Segment identities aggressively
- Eliminate passwords where possible
- Plan for identity disaster recovery
Next Part: Emerging Threat Landscape: AI, Supply Chain, and Cloud-Native Identity Attacks
Emerging Threat Landscape Targeting Entra ID Security 2026
Entra ID Security 2026 exists in a threat landscape fundamentally different from today. Attackers are no longer experimenting with identity abuse — they are perfecting it.
The future identity threat landscape is defined by three forces:
- Artificial intelligence
- Cloud-native attack surfaces
- Trust-based exploitation rather than vulnerability exploitation
Understanding these threats is the foundation of defending against them.
AI-Powered Identity Attacks
By 2026, artificial intelligence will dramatically accelerate identity-based attacks. AI will not replace attackers — it will amplify them.
How AI Changes Entra ID Threats
- Real-time phishing page generation
- Perfectly localized impersonation emails
- Automated MFA fatigue campaigns
- Behavior-mimicking login attempts
Traditional phishing detection relies on identifying anomalies. AI removes anomalies.
This makes Entra ID Security 2026 dependent on phishing-resistant authentication and behavioral analysis.
Consent Phishing 2.0
OAuth consent phishing is one of the most dangerous identity attack vectors.
In 2026, attackers will:
- Register legitimate-looking applications
- Request minimal but powerful permissions
- Leverage user trust in branded login flows
- Maintain persistence without passwords
Because OAuth tokens are legitimate, traditional MFA offers no protection.
Organizations must strictly govern OAuth permissions as part of Entra ID Security 2026.
Supply Chain Identity Compromise
Supply chain attacks no longer target software binaries — they target identity trust.
How Identity Supply Chain Attacks Work
- Third-party SaaS compromise
- Federated trust abuse
- Compromised managed identities
- Excessive cross-tenant permissions
A single compromised vendor identity can expose hundreds of tenants.
This makes identity trust relationships a high-risk surface in Entra ID Security 2026.
Workload Identity Abuse
Workload identities (service principals, managed identities) are exploding in usage.
Unfortunately, they are also poorly governed.
Why Workload Identities Are Dangerous
- No MFA enforcement
- Long-lived secrets
- Rarely monitored
- Often over-privileged
Attackers prefer workload identities because they provide silent persistence.
Entra ID Security 2026 must treat workload identities as first-class security subjects.
Token Theft and Session Hijacking
Passwords are no longer the primary target — tokens are.
Attackers steal:
- Access tokens
- Refresh tokens
- Session cookies
Once stolen, tokens allow:
- Bypassing MFA
- Persistent access
- Invisible lateral movement
Continuous Access Evaluation (CAE) becomes critical for Entra ID Security 2026.
Hybrid Identity Exploitation
Hybrid identity remains one of the largest risk multipliers.
Common Hybrid Attack Paths
- On-prem AD compromise → Entra ID sync abuse
- Password hash synchronization attacks
- Federation trust exploitation
- Stale synced identities
Attackers move from on-prem to cloud faster than defenders detect.
Hybrid identity must be hardened aggressively or reduced.
For hybrid security guidance, see: Hybrid Entra ID security best practices
PowerShell: Detect High-Risk Service Principals
Get-MgServicePrincipal |
Where-Object {$_.PasswordCredentials.Count -gt 0} |
Select DisplayName, AppId
This helps identify legacy secret-based workload identities.
Graph API: Monitor Sign-In Anomalies
Invoke-MgGraphRequest -Method GET ` -Uri "https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/auditLogs/signIns"
Behavioral analysis of sign-ins is mandatory for Entra ID Security 2026.
FAQs – Emerging Threats
Are passwords already obsolete?
For privileged access, yes. Password-only authentication is already unsafe.
Are service principals more dangerous than users?
Often yes, because they lack visibility and governance.
Can AI attacks be detected?
Only through behavioral analytics and phishing-resistant authentication.
Key Points – Part 4
- AI removes traditional attack anomalies
- OAuth and tokens are prime attack targets
- Supply chain trust is a critical risk
- Hybrid identity amplifies attack surface
Next Part: Advanced Detection, Monitoring, and Threat Hunting for Entra ID Security 2026
Advanced Detection, Monitoring, and Threat Hunting for Entra ID Security 2026
Entra ID Security 2026 cannot rely on perimeter alerts or static rules. Identity-based attacks blend into legitimate activity, making traditional detection models ineffective.
In 2026, successful identity defense depends on continuous monitoring, behavioral analytics, and proactive threat hunting. This section explores how organizations must evolve detection strategies for modern identity threats.
Why Traditional Monitoring Fails
Legacy security monitoring focuses on:
- Failed login attempts
- Malware alerts
- Network anomalies
Identity attackers rarely trigger these alerts. They authenticate successfully.
This creates a dangerous blind spot in Entra ID Security 2026.
Identity Telemetry Strategy
Effective detection begins with collecting the right identity signals.
Critical Identity Signals
- Sign-in logs (interactive & non-interactive)
- Audit logs
- Risk detections
- OAuth consent events
- Role activations (PIM)
- Conditional Access evaluations
Without full telemetry, threat hunting becomes guesswork.
For telemetry architecture guidance, see: Entra ID monitoring strategy
Behavioral Analytics: The Core of Future Detection
Static rules fail when attackers mimic normal behavior. Behavioral analytics focuses on:
- Baseline user behavior
- Deviation detection
- Impossible travel correlation
- Session duration anomalies
In Entra ID Security 2026, detection shifts from “what happened” to “what is unusual.”
Microsoft Entra ID Identity Protection Deep Dive
Identity Protection provides built-in risk assessment for:
- Users
- Sign-ins
Risk signals include:
- Anonymous IP usage
- Malware-linked IPs
- Atypical travel
- Leaked credentials
However, Identity Protection must be combined with Conditional Access automation.
Risk-Based Access Enforcement
- Low risk → allow
- Medium risk → require MFA
- High risk → block or require password reset
Risk-based enforcement is foundational for Entra ID Security 2026.
Threat Hunting: From Alerts to Hypotheses
Threat hunting assumes compromise and searches for evidence.
Common Identity Hunting Hypotheses
- Service principals with abnormal sign-in patterns
- Privileged role activation outside business hours
- OAuth apps with unusual consent spikes
- Refresh token reuse across locations
Threat hunting must be continuous, not reactive.
PowerShell: Detect Privileged Role Activations
Get-MgAuditLogDirectoryAudit |
Where-Object {$_.ActivityDisplayName -like "*Activate*"} |
Select ActivityDisplayName, InitiatedBy, ActivityDateTime
Monitoring PIM activity is critical for Entra ID Security 2026.
Graph API: Analyze OAuth Consent Events
Invoke-MgGraphRequest -Method GET ` -Uri "https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/auditLogs/directoryAudits"
OAuth abuse often hides in audit logs.
SIEM Integration: Identity as a First-Class Signal
Identity logs must be integrated into SIEM platforms.
Correlation Use Cases
- Endpoint + identity correlation
- Impossible travel + token reuse
- Admin role activation + data exfiltration
SIEM without identity context is blind in Entra ID Security 2026.
Continuous Access Evaluation (CAE)
CAE enables real-time session revocation when risk changes.
Use cases:
- User risk becomes high mid-session
- Account disabled during active session
- Password reset triggered
CAE closes the window attackers exploit after authentication.
FAQs – Detection & Monitoring
Is Identity Protection enough?
No. It must be augmented with custom analytics and hunting.
Should every tenant use a SIEM?
For enterprises, yes. Identity signals must be centralized.
How often should threat hunting occur?
Continuously, with weekly focused hypotheses.
Key Points – Part 5
- Identity telemetry is non-negotiable
- Behavioral analytics outperform static rules
- Threat hunting must be proactive
- CAE reduces session-based attacks
Next Part: Governance, Compliance, and Least Privilege at Scale for Entra ID Security 2026
Governance, Compliance, and Least Privilege at Scale for Entra ID Security 2026
Entra ID Security 2026 is unsustainable without strong governance. Security controls fail when identities accumulate permissions unchecked.
In modern enterprises, the greatest risk is not malicious insiders or hackers — it is excessive access combined with lack of visibility.
The Identity Governance Crisis
Most organizations suffer from:
- Privilege creep
- Stale accounts
- Unused admin roles
- Overprivileged service principals
These issues are invisible until exploited.
Entra ID Security 2026 requires governance to be continuous, automated, and measurable.
Identity Lifecycle Management
Every identity has a lifecycle:
- Creation
- Access assignment
- Modification
- Deprovisioning
Security failures occur when lifecycle events are manual.
Automation Imperatives
- HR-driven provisioning
- Role-based access assignment
- Automatic access expiration
- Immediate deprovisioning on exit
Identity lifecycle automation directly supports Entra ID Security 2026.
Least Privilege as a Living Policy
Least privilege is often treated as a one-time exercise. This is a mistake.
Permissions must change as roles change.
Least Privilege Enforcement Methods
- Just-In-Time access (PIM)
- Access expiration
- Approval workflows
- Risk-based elevation
Standing access is the enemy of identity security.
Privileged Identity Management (PIM)
PIM is mandatory for privileged roles in Entra ID Security 2026.
Capabilities include:
- Eligible vs Active roles
- Approval-based activation
- Time-bound access
- Audit trails
Every Global Admin should be eligible — never permanently active.
PowerShell: Audit Standing Privileged Access
Get-MgRoleManagementDirectoryRoleAssignment |
Where-Object {$_.AssignmentState -eq "Active"} |
Select PrincipalId, RoleDefinitionId
Any permanent assignment is a risk.
Access Reviews at Scale
Manual access reviews do not scale.
Access reviews must be:
- Automated
- Risk-prioritized
- Outcome-driven
Review targets:
- Guest users
- Privileged roles
- Application access
- Service principals
Governance without enforcement is theater.
Compliance Alignment
Entra ID Security 2026 supports compliance frameworks:
- ISO 27001
- NIST 800-53
- SOC 2
- GDPR
However, compliance does not equal security.
Compliance controls must reinforce real-world defense.
Official Microsoft compliance guidance: Microsoft Entra Identity Governance
Workload Identity Governance
Workload identities often bypass governance.
Controls required:
- Permission review automation
- Secret expiration enforcement
- Certificate-based authentication
- Usage monitoring
Service principals must be governed like human admins.
Graph API: Identify Overprivileged Apps
Invoke-MgGraphRequest -Method GET ` -Uri "https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/applications"
Cross-reference permissions with actual usage.
FAQs – Governance & Compliance
Is PIM mandatory?
Yes. Permanent admin access is indefensible in 2026.
Do access reviews prevent breaches?
They reduce attack surface dramatically.
Should guests have PIM?
Guest access must be time-bound and reviewed.
Key Points – Part 6
- Governance must be automated
- Standing access must be eliminated
- PIM is foundational
- Compliance should reinforce security
Next Part: Hybrid Identity, Legacy Risk, and Migration Strategy for Entra ID Security 2026
Hybrid Identity, Legacy Risk, and Migration Strategy for Entra ID Security 2026
Entra ID Security 2026 is fundamentally incompatible with uncontrolled hybrid identity. While hybrid identity enabled cloud adoption, it has also become one of the most exploited attack surfaces.
Attackers no longer differentiate between on-premises and cloud identities — they exploit the trust between them.
Why Hybrid Identity Increases Risk
Hybrid identity introduces:
- Additional trust boundaries
- Synchronization dependencies
- Multiple authentication stacks
- Expanded credential attack surface
A single compromise in on-prem AD can cascade into Entra ID.
Common Hybrid Attack Paths
- On-prem AD admin compromise → Entra ID sync abuse
- Password hash synchronization theft
- Federation certificate compromise
- Stale synced privileged accounts
In Entra ID Security 2026, hybrid trust must be minimized.
Federation vs Cloud Authentication
Federation adds complexity and risk.
- Federation servers become critical infrastructure
- Certificates become high-value targets
- Outages impact authentication globally
Cloud-based authentication with phishing-resistant MFA is the preferred model.
Reducing Hybrid Blast Radius
- Limit synced accounts
- Disable legacy protocols
- Use cloud-only admin accounts
- Monitor Entra Connect health
Hybrid identity should be a transition state, not a permanent architecture.
PowerShell: Identify High-Risk Synced Accounts
Get-MgUser | Where-Object {
$_.OnPremisesSyncEnabled -eq $true -and $_.AccountEnabled -eq $true
}
Migration Strategy for 2026
A secure migration strategy includes:
- Phased cloud-only authentication
- Passwordless rollout
- Privileged account isolation
- Gradual federation retirement
FAQs – Hybrid Identity
Should hybrid identity be eliminated?
Eventually yes. Minimize it aggressively.
Is Entra Connect still required?
Only where legacy dependencies exist.
Key Points – Part 7
- Hybrid identity multiplies risk
- Federation is increasingly unsafe
- Cloud-only auth is the future
Next Part: Operational Security, Incident Response, and Identity DR for Entra ID Security 2026
Operational Security, Incident Response, and Identity DR for Entra ID Security 2026
Entra ID Security 2026 fails without operational readiness. Detection without response is security theater.
Identity-First Incident Response
Identity incidents require immediate action:
- Token revocation
- Session invalidation
- Role de-escalation
- OAuth permission removal
PowerShell: Emergency Session Revocation
Revoke-MgUserSignInSession -UserId user@domain.com
Break-Glass Response Strategy
- Offline MFA-protected accounts
- No Conditional Access restrictions
- Continuous monitoring
Identity Disaster Recovery Planning
Identity DR must include:
- Role assignment backups
- Policy versioning
- Audit log retention
FAQs – Identity Operations
How fast must identity response be?
Minutes, not hours.
Should DR be tested?
Quarterly at minimum.
Key Points – Part 8
- Identity response must be immediate
- Break-glass accounts are mandatory
- DR planning is non-optional
Next Part: Your Call to Action: Securing Entra ID for 2026 and Beyond
Your Call to Action: Securing Entra ID for 2026 and Beyond
Entra ID Security 2026 is not a future problem. It is a present decision.
Immediate Actions You Must Take Today
- Enable phishing-resistant MFA
- Audit all privileged roles
- Govern OAuth and service principals
- Eliminate standing access
Strategic Security Investments
- Identity governance automation
- Behavioral analytics
- Passwordless rollout
- Threat hunting maturity
Building a Future-Proof Identity Culture
Security is cultural.
- Identity ownership clarity
- Security-first access design
- Continuous education
The Cost of Inaction
Organizations that fail to modernize identity security will:
- Suffer silent breaches
- Lose regulatory trust
- Face operational paralysis
Final FAQs
Is Entra ID secure by default?
No. Security is optional unless enforced.
Can small orgs apply these principles?
Yes. Identity attacks do not discriminate.
Final Key Takeaways
- Identity is the new perimeter
- 2026 attackers will authenticate, not exploit
- Zero Trust must evolve
- Governance equals survivability
Final Thought: If you design identity assuming trust, attackers will exploit it. If you design identity assuming compromise, attackers will fail.
This is the essence of Entra ID Security 2026.




Leave a Reply