Why Cloud Migration is the New Normal.
As businesses grow, their on-premises infrastructure often becomes a bottleneck due to high maintenance, limited scalability, and slower deployment cycles. Migrating to the cloud unlocks agility, operational efficiency, and cost savings.
According to Gartner, over 85% of enterprises will have adopted a cloud-first strategy by 2025.
Key Drivers of Cloud Migration:
-
Scalability: Expand or shrink resources instantly
-
Business Continuity: Disaster recovery and high availability
-
Innovation: Access to AI/ML, big data, and analytics tools
-
Cost Savings: Pay only for what you use
-
Security: Advanced tools for compliance, encryption, and access control
Pre-Migration Phase: Assess, Plan, and Prepare
Before migrating anything, conduct a thorough cloud readiness assessment.
1. Inventory Audit
Use discovery tools to identify:
-
All hardware and virtual machines
-
Network topology
-
Application dependencies
-
Storage volumes
-
Operating systems and licensing
Tool Tip: Use Azure Migrate or AWS Application Discovery Service for automated inventory analysis.
2. Application Dependency Mapping
Map the communication between apps, databases, APIs, and backend services to:
-
Avoid missed dependencies
-
Ensure minimal downtime during migration
-
Design an effective cutover plan
3. Choose Your Migration Approach
Let’s break down the 6R strategies that guide every successful cloud migration.
Migration Planning Phase
This phase ensures your migration won’t break systems, violate security, or cause outages.
1. Define Clear Goals & Metrics
-
Reduce cost by 30%?
-
Improve app uptime to 99.99%?
-
Faster release cycles?
Align business, technical, and operational teams.
2. Select Your Cloud Provider
Consider:
-
Compliance needs (GDPR, HIPAA)
-
Data sovereignty
-
SLA and support options
3. Design Cloud Architecture
Things to define:
-
VNet/Subnet structure
-
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
-
Resource Groups & Tags
-
Security controls (MFA, conditional access)
-
Backup & DR strategy
Create sandbox environments for testing before production migration.
Cloud Foundation Setup
-
Create Cloud Subscriptions/Accounts
-
Set billing alerts and budgets
-
-
IAM and RBAC Configuration
-
Create least-privileged roles
-
Enable audit logging
-
-
Virtual Network Configuration
-
Plan IP ranges
-
Setup peering if hybrid
-
-
Set Up Monitoring Tools
-
Azure Monitor, Log Analytics
-
AWS CloudWatch & CloudTrail
-
-
Backup Plan
-
Configure snapshot and geo-redundancy
-
Step-by-Step Cloud Migration Process
Step 1: Migrate Non-Critical Apps First
Start with internal apps like:
-
Intranet
-
File servers
-
Dev/Test environments
This helps you test your migration pipeline.
Step 2: Data Migration
Options:
-
Offline Transfer: Physical devices like Azure Data Box, AWS Snowball
-
Online Transfer: VPN or ExpressRoute/DirectConnect for real-time sync
Tools:
-
Azure Database Migration Service
-
AWS Database Migration Service (DMS)
-
GCP Transfer Appliance
Tip: Use parallel testing during data sync to ensure consistency.
Step 3: VM/Server Migration
-
Use Azure Migrate or CloudEndure for VM replication
-
Choose between:
-
Cold migration: Shut down → copy → power on in cloud
-
Live migration: No downtime (if supported)
-
Set cutover date and communicate with stakeholders.
Step 4: Testing & Validation
Test all layers:
-
Connectivity: Can users access?
-
Functionality: Is the app working as expected?
-
Performance: Latency, throughput, CPU/memory usage
-
Security: Verify firewall rules, roles, encryption
Prepare rollback plan if errors occur.
Step 5: Go Live & Optimize
Once stable:
-
Route production traffic
-
Monitor logs, costs, and metrics
-
Scale based on demand
Enable auto-scaling and configure cost control policies (e.g., shut down unused VMs)
Popular Cloud Migration Tools
Common Cloud Migration Challenges & Solutions
Post-Migration Optimization
Enable Cost Management
-
Azure Cost Management + Billing
-
AWS Cost Explorer
-
-
Set Up Auto Scaling
-
VMs, databases, containers (AKS, EKS, GKE)
-
-
Security Audits
-
Run compliance checks using tools like Defender for Cloud, AWS Config
-
-
Performance Tuning
-
Move to managed services (App Services, RDS, Cosmos DB)
-
Cache layers (Redis, CDN)
-
Cloud Migration Best Practices
- Test early, test often
- Document every step and dependency
- Implement Zero Trust and strong IAM policies
- Communicate regularly across teams
- Monitor usage and right-size resources
- Backup before every major migration
- Update security and cost reviews monthly
FAQs About Cloud Migration
Q1: What’s the fastest way to migrate from on-prem to cloud?
A: Rehost (lift-and-shift) using native migration tools is typically the fastest and simplest method.
Q2: How do I migrate a legacy app not compatible with the cloud?
A: Consider using refactoring, containers, or replacing it with a SaaS-based solution.
Q3: How can I minimize downtime during migration?
A: Use real-time data sync tools like Azure Site Recovery or CloudEndure with a well-tested cutover plan.
Q4: Can I keep some workloads on-prem?
A: Yes, hybrid cloud models are supported using Azure Arc, AWS Outposts, or GCP Anthos.
Real Case Study: Financial Firm Migrating to Azure
-
Client: Mid-sized investment firm
-
Migration Type: Rehost + Refactor
-
Tools Used: Azure Migrate, ASR, Azure Synapse
-
Results:
-
50% cost saving in 12 months
-
Improved backup and recovery
-
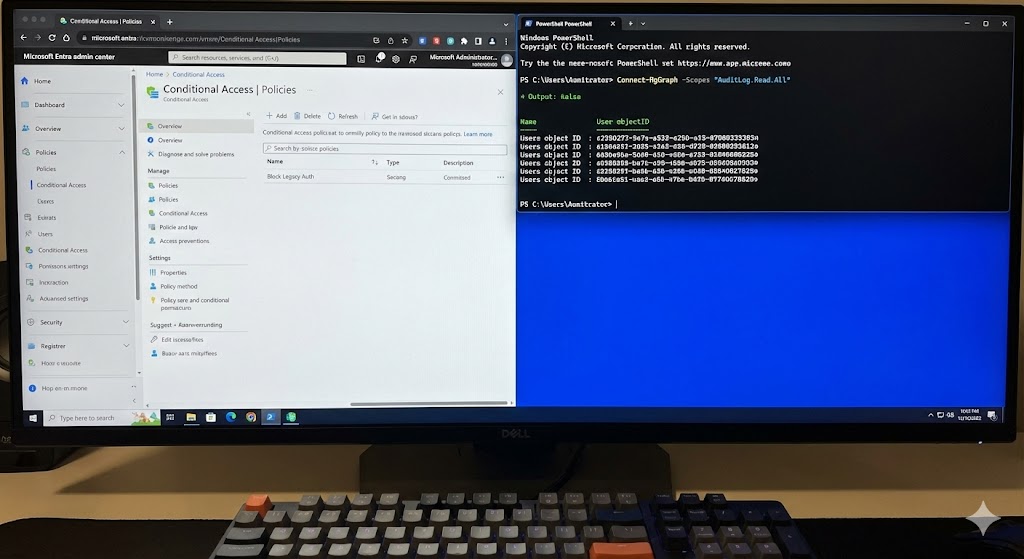
Enhanced security with Conditional Access and MFA
-
Final Thoughts
Migrating to the cloud is a journey—not a one-time event. With a proper assessment, the right strategy (6 Rs), and phased implementation, you can move seamlessly and securely to the cloud while maximizing ROI.
#CloudMigration #Azure #AWS #GoogleCloud #CloudComputing #CloudStrategy #EntraID #DevOps #LiftAndShift






Leave a Reply