Introduction to IAM in AWS
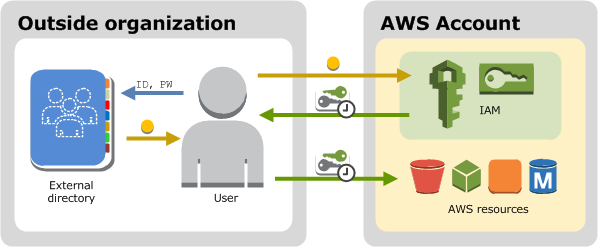
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a secure and scalable service that enables you to manage access to AWS resources.
Using IAM, you can control who can sign in (authentication) and what actions they can perform (authorization) in your AWS environment.
IAM is the foundation of AWS security. Whether you’re managing developers, admins, or applications, IAM ensures that every user or service has only the permissions they need — and nothing more.
Learn more about IAM and cloud security best practices on Cloud Knowledge.

What are IAM Services in AWS?
AWS IAM is not a single feature — it’s a suite of access management tools that help define and enforce access control.
Here are the core IAM services in AWS:
What are IAM Services in AWS?
AWS IAM is not a single feature — it’s a suite of access management tools that help define and enforce access control.
Here are the core IAM services in AWS:
IAM Users
IAM Users are entities representing individuals or applications that interact with AWS services.
Each user has unique credentials — a username, password, and optionally, access keys for CLI or API access.
Best Practices for IAM Users:
Avoid using the root account for daily operations.
Assign least privilege permissions.
Enable MFA for all users.
Rotate access keys regularly.
IAM Groups
IAM Groups simplify permission management for multiple users.
For example, you can create:
-
Developersgroup → access to EC2, S3 -
Financegroup → access to billing and cost explorer
When a user joins a group, they inherit all policies attached to that group.
This makes it easy to apply consistent permissions across teams.
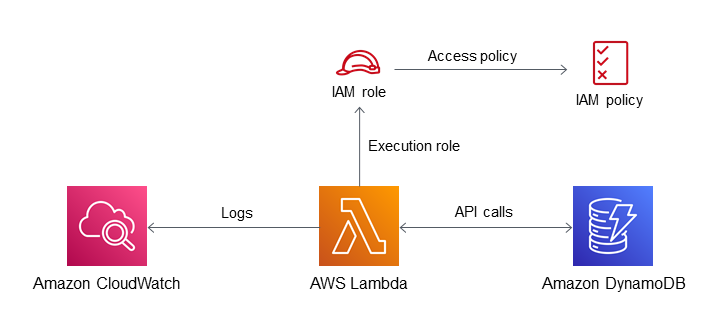
IAM Roles in AWS
What Are Roles in AWS?
IAM Roles are temporary access credentials that AWS services, users, or applications can assume to perform tasks without using long-term credentials.
Roles are essential for:
Cross-account access
Temporary access for applications or EC2 instances
AWS service permissions (like Lambda, EC2, ECS tasks)
How Roles Work:
Create an IAM Role and define trust relationships (who can assume the role).
Attach Policies to define permissions.
AWS issues temporary security tokens to whoever assumes the role.
Types of IAM Roles in AWS
AWS offers different role types based on use cases:
Example:
A Lambda function can assume a role that allows it to access Amazon S3 for reading/writing files — without storing access keys.
How to Customize IAM Roles
You can customize IAM roles to match your organization’s security model and least privilege principle.
Steps to Customize IAM Roles:
Go to AWS Console → IAM → Roles.
-
Create Role → Choose Trusted Entity:
-
AWS Service
-
Another AWS Account
-
Web Identity or SAML Provider
-
-
Attach Policies – AWS Managed or Custom JSON.
-
Define Trust Relationship – specify who can assume the role.
-
Review and Create Role.
Example: Custom Role for EC2 Access
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:PutObject"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::mybucket/*"
}
]
}IAM Policies in AWS
IAM Policies are JSON-based documents that define permissions for users, groups, or roles.
Each policy contains statements defining:
-
Effect – Allow or Deny
-
Action – API actions (like
s3:GetObject) -
Resource – AWS resources
-
Condition – Optional filters for fine-grained access
- Types of Policies:

Example: S3 Read-Only Access Policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["s3:GetObject"],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::example-bucket/*"
}
]
}Security Best Practices for IAM
-
Enable MFA for all IAM users.
-
Rotate credentials regularly.
-
Use roles instead of long-term access keys.
-
Apply the principle of least privilege (only give needed permissions).
-
Use IAM Access Analyzer to detect overly permissive policies.
-
Monitor IAM activity via AWS CloudTrail and IAM Access Advisor.
Conclusion
AWS IAM is the backbone of secure cloud access.
By effectively using users, groups, roles, and policies, organizations can implement strong access control and minimize security risks.
Customizing IAM roles and policies ensures your AWS environment stays compliant, secure, and efficient.
Explore more AWS security tutorials and IAM configuration guides on Cloud Knowledge.





Leave a Reply