Single Sign-On (SSO) is a powerful feature in Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure Active Directory) that allows users to sign in once and access multiple applications without being prompted for credentials again. However, when something goes wrong, diagnosing SSO failures can be complex.
This guide will walk you through a comprehensive approach to troubleshooting SSO for both Azure App Registrations and Enterprise Applications. We will cover the types of errors, how to interpret logs, configuration checks, common pitfalls, and real-world solutions.
Understanding the Basics of SSO in Azure
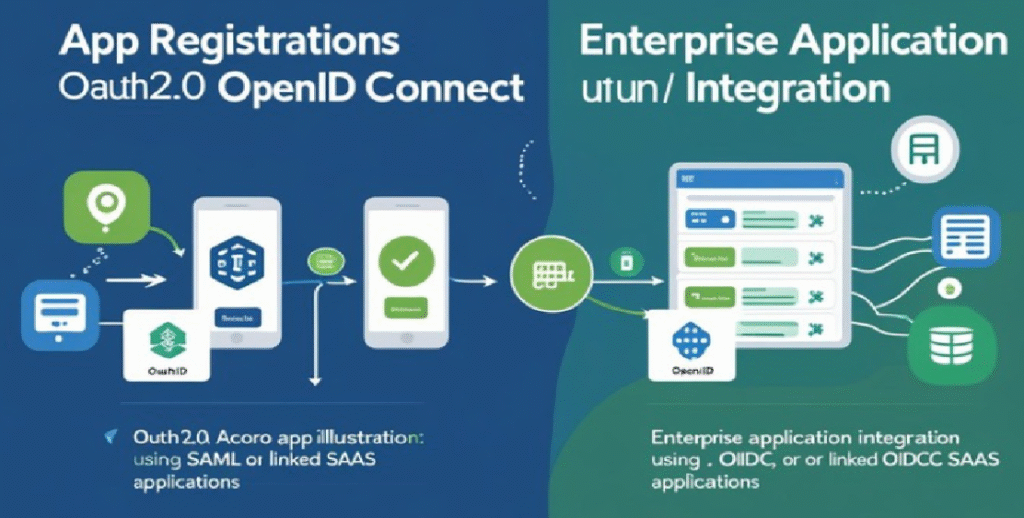
Before diving into troubleshooting, it’s important to understand the types of SSO integrations supported in Microsoft Entra ID:
1. App Registrations (OAuth 2.0 / OpenID Connect)
-
Used for custom or third-party applications where you control the code or APIs.
-
Primarily token-based (JWT), using scopes, permissions, and authorization endpoints.
-
Applications get registered under Azure AD → App Registrations.
2. Enterprise Applications (SAML, OIDC, or Linked SaaS apps)
-
Often used for integrating with SaaS services (e.g., Salesforce, ServiceNow).
-
Supports SAML 2.0 and sometimes OpenID Connect or password-based SSO.
-
Managed under Azure AD → Enterprise Applications.
Both approaches can experience SSO failures if not configured correctly.
Common SSO Problems in Azure and Their Root Causes
1. Login Fails with AADSTS Errors
Symptoms:
“AADSTS50011: The reply URL specified in the request does not match…”
“AADSTS50105: User is not assigned to the application.”
“AADSTS700016: Application with identifier not found.”
Root Causes:
Mismatched reply URL or redirect URI.
Users not assigned to the app.
Incorrect Client ID or tenant configuration.

2. Token Validation Issues
Symptoms:
-
Token rejected by app: “Invalid audience”, “Invalid signature”.
-
Expired token errors.
-
Incorrect user claims or missing attributes.
Root Causes:
-
Wrong
aud(audience) oriss(issuer) values in the app. -
App not trusting Azure token signing keys.
-
Missing optional claims in Azure AD configuration.
3. SAML Assertion Failures
Symptoms:
-
“Invalid NameID format”, “Missing required claim“, “Invalid SAML response“.
-
App cannot parse or validate the assertion.
Root Causes:
-
Claims not mapped correctly.
-
Mismatched Entity ID or Reply URL.
-
Expired SAML certificate.

4. Redirection Loop or Authentication Loop
Symptoms:
-
User is redirected repeatedly between Azure login and the application.
-
Browser throws “Too many redirects” or similar errors.
Root Causes:
-
Wrong session/cookie handling in the app.
-
Incorrect redirect URIs.
-
Custom domain or proxy misconfiguration.

User Not Authorized or Not Assigned
Symptoms:
-
“Access Denied” after successful authentication.
-
Application redirects to an error page even though user logs in successfully.
Root Causes:
-
Application access restricted to assigned users.
-
Conditional Access blocking access based on device, location, etc.

Step-by-Step SSO Troubleshooting in Azure
Step 1: Identify the Application Type
-
Go to Azure Portal → Azure Active Directory → Enterprise Applications or App Registrations.
-
Check:
-
Is the app integrated via SAML or OpenID Connect (OIDC)?
-
Is it App registration (mostly token-based) or Enterprise Application (mainly SAML-based)?
-
Step 2: Check Sign-In Logs
-
Navigate to: Azure AD → Sign-in logs
-
Filter by the user or app name.
-
Click on the failed entry and review:
-
Status: Failure or Success
-
Error code and message (e.g., AADSTS50011)
-
Conditional Access policies applied
-
Token or SAML details
Step 3: Validate Application Configuration
For App Registrations:
-
Check the Redirect URIs under Authentication
-
Ensure correct supported account type:
-
Single tenant or multi-tenant
-
-
Under API permissions:
-
Add required scopes (e.g.,
openid,profile,User.Read) -
Click Grant admin consent
For Enterprise Applications:
-
Go to: Azure AD → Enterprise Applications → Your App
-
Under Single sign-on:
-
Verify Identifier (Entity ID) and Reply URL
-
Check SAML certificate validity
-
Review user attribute mappings (claims)
-
Step 4: Validate Claims and Tokens
For SAML Apps:
-
Use browser extension like SAML-tracer (Firefox/Chrome).
-
Inspect the SAML Response and Assertion.
-
Validate:
-
NameIDformat -
Required attributes (
email,userprincipalname, etc.) -
Signature, Audience, Issuer
-
For OIDC Apps:
-
Decode JWT token using https://jwt.io
-
Check:
-
aud(Audience) -
iss(Issuer) -
exp(Expiration) -
Claims like
email,groups,upn
Step 5: Check User Assignments
If the application is restricted:
-
Assign specific users or security groups.
If the app is not restricted, toggle off the setting:
Step 6: Review Conditional Access Policies
-
Check if:
-
Access is blocked based on location, device state, risk level.
-
App is targeted by a restrictive policy.
-
You can simulate access using “What If” tool under Conditional Access.
Step 7: Test Manually and Log Everything
For SAML:
Use:
https://login.microsoftonline.com/<tenant-id>/saml2
Common Real-World Scenarios & Fixes
Scenario 1: SAML app shows “Invalid NameID format”
Fix: Go to Enterprise App → SSO → Attributes & Claims → Change NameID format to emailAddress or Persistent.
Scenario 2: User redirected endlessly between app and login page
Fix:
-
Check browser cookies or session storage
-
Ensure app properly initiates and consumes the token or assertion
-
Confirm redirect URIs are correct and HTTPS is enforced
Scenario 3: App throws “Invalid Audience” error
Fix:
-
Ensure app is checking the correct
audclaim -
In Expose an API tab, ensure Application ID URI matches audience
Best Practices to Avoid SSO Issues
-
Always match redirect URIs and entity IDs exactly.
-
Renew certificates before expiry.
-
Use Azure AD Sign-in logs for all troubleshooting.
-
Don’t forget to assign users or groups to apps.
-
Use environment-specific app registrations (test, dev, prod).
-
Automate configuration checks via PowerShell or Bicep.
-
Document changes made in app integrations.
Conclusion
SSO is a powerful feature that enhances security and user experience when configured properly. But when it fails, the fix lies in identifying whether it’s a configuration mismatch, token issue, or access policy misfire.
By following this guide, you can systematically diagnose and resolve issues in both App Registrations and Enterprise Applications integrated with Microsoft Entra ID. Whether it’s decoding tokens, inspecting logs, or correcting claims, each step gets you closer to seamless access.
Need help implementing SSO for your app? Or want an automated health-check script for your enterprise apps? Reach out to us for personalized support.












Leave a Reply