Fully Managed Relational Database Cloud SQL – The Ultimate 2025 Enterprise Guide for Architects, Developers & Cloud Engineers
The world of enterprise applications is rapidly evolving, and organizations are shifting from manually managed databases toward cloud-native, automated platforms that provide high availability, scalability, security, and performance intelligence. One of the most powerful solutions in this category is Fully Managed Relational Database Cloud SQL — a robust, production-grade service that simplifies running relational databases at scale.
This guide breaks down everything you need to know about Fully Managed Relational Database Cloud SQL, covering architecture, HA internals, replication, advanced tuning, security hardening, migration patterns, VPC integration, cost optimization, performance troubleshooting, and automated operations using PowerShell, gcloud CLI, SQL scripts, and REST APIs.
Whether you manage MySQL, PostgreSQL, or SQL Server workloads, this comprehensive 2025 guide will help you deploy and maintain fully optimized and production-ready databases.

1. What is Fully Managed Relational Database Cloud SQL?
Fully Managed Relational Database Cloud SQL is a managed service that helps organizations run MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server without handling infrastructure provisioning, patching, updates, backups, replication, failover, security configuration, or OS-level maintenance. It frees teams from traditional database administration tasks while providing maximum uptime, reliability, and governed access.
Databases are deployed on Google Cloud’s high-performance compute platform with SSD-backed storage, global networking, and strong integration with observability, security, and automation services.
Key Advantages
- Zero-server maintenance and fully automated operations
- Resilient, multi-zone high availability built in
- Automated backups, PITR, and maintenance windows
- IAM-integrated security and VPC-level isolation
- Elastic compute and storage scalability
- Performance optimization using Query Insights and logs
- Cross-region replication and read scaling
- Simple provisioning via console, CLI, Terraform, or API
Key Points Summary
- Supports MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server
- Ideal for enterprise transactional systems
- 99.95% uptime SLA for high availability
- Fully integrated with Google Cloud ecosystem
- Suitable for microservices, SaaS, analytics, and ERP workloads
FAQs
Q1: Is Fully Managed Relational Database Cloud SQL suitable for large enterprises?
Yes. It is built to handle mission-critical workloads with high availability, replication, and security controls.
Q2: Can I scale Cloud SQL without downtime?
Compute and storage scaling are live operations, and automatic storage resizing happens without downtime.
2. Supported Database Engines in Fully Managed Relational Database Cloud SQL
Cloud SQL supports three of the most widely-used relational database engines. These engines are fully optimized for performance, security, and scalability with minimal operational effort.
2.1 MySQL
Cloud SQL offers multiple MySQL versions, global read replicas, automated failovers, and SSD-backed persistent storage for low-latency I/O. Use cases include e-commerce platforms, CMS workloads, and lightweight OLTP workloads.
2.2 PostgreSQL
Known for strong ACID guarantees, advanced indexing, JSONB support, and powerful analytical capabilities, Cloud SQL PostgreSQL is ideal for microservices, data analytics, and event-driven architectures.
2.3 SQL Server
Cloud SQL for SQL Server supports Windows authentication, SQL Agent, Always On availability groups, and high-performance transactional processing.
Key Points Summary
- Managed MySQL supports read replicas and cross-region reads
- Managed PostgreSQL supports logical replication and PITR
- Managed SQL Server supports Always On HA and SQL Agent
- All engines support IAM-based access
FAQs
Q: Can I migrate MySQL to Cloud SQL without downtime?
Yes, using Database Migration Service (DMS) with CDC (change data capture).
3. High Availability (HA) Architecture in Fully Managed Relational Database Cloud SQL
High Availability ensures your database withstands infrastructure failures, zonal outages, or maintenance events. Cloud SQL automatically provisions a primary instance and a hot-standby replica in another zone.
3.1 HA Internal Architecture Flow
+------------------------+ synchronous +------------------------+
| Primary Instance | ------------------> | Standby Instance |
| Zone A (Active Node) | | Zone B (Hot Standby) |
+------------------------+ +------------------------+
| |
| automatic failover |
+------------------------>-----------------------+
A failover is triggered if:
- The primary VM crashes
- Zone outage occurs
- Maintenance window triggers a failover
- Health checks detect primary unresponsiveness
Key Technical Points
- Failover time typically 5–30 seconds
- Standby is always synchronous for strong consistency
- Connection strings update automatically (using private IP)
- No manual failover steps required
FAQs
Q: Can I force failover for testing?
Yes, using the SQL Admin API or gcloud CLI.
4. Scalability in Fully Managed Relational Database Cloud SQL
Cloud SQL supports vertical and horizontal scaling to meet application demand as workloads grow.
4.1 Vertical Scaling
Increase CPU cores and memory to handle increased connections or high transactional workloads. Adaptive autoscaling ensures workloads keep running optimally.
4.2 Horizontal Scaling Using Read Replicas
Read replicas reduce load on the primary instance and help achieve global low-latency access.
- Cross-region read replicas
- Read scaling for analytics/reporting
- Traffic balancing using application logic or read routing
Automatic Storage Increases
Storage automatically scales when nearing defined thresholds. No downtime, no manual intervention.
Key Points Summary
- Scale CPU/RAM without downtime
- Add read replicas for heavy read workloads
- Automatic storage resizing avoids outages
5. Backup Strategy & Point-in-Time Recovery (PITR)
Cloud SQL provides daily automated backups, continuous transaction log backups, and fast point-in-time restoration.
Backup Features
- Automated daily backups
- Manual on-demand backups
- Continuous transaction log archiving
- PITR for granular restore operations
- Cross-region backup redundancy
Key Points Summary
- PITR protects against accidental deletions
- Backups stored in highly durable storage
- Retention configurable from 7–365 days
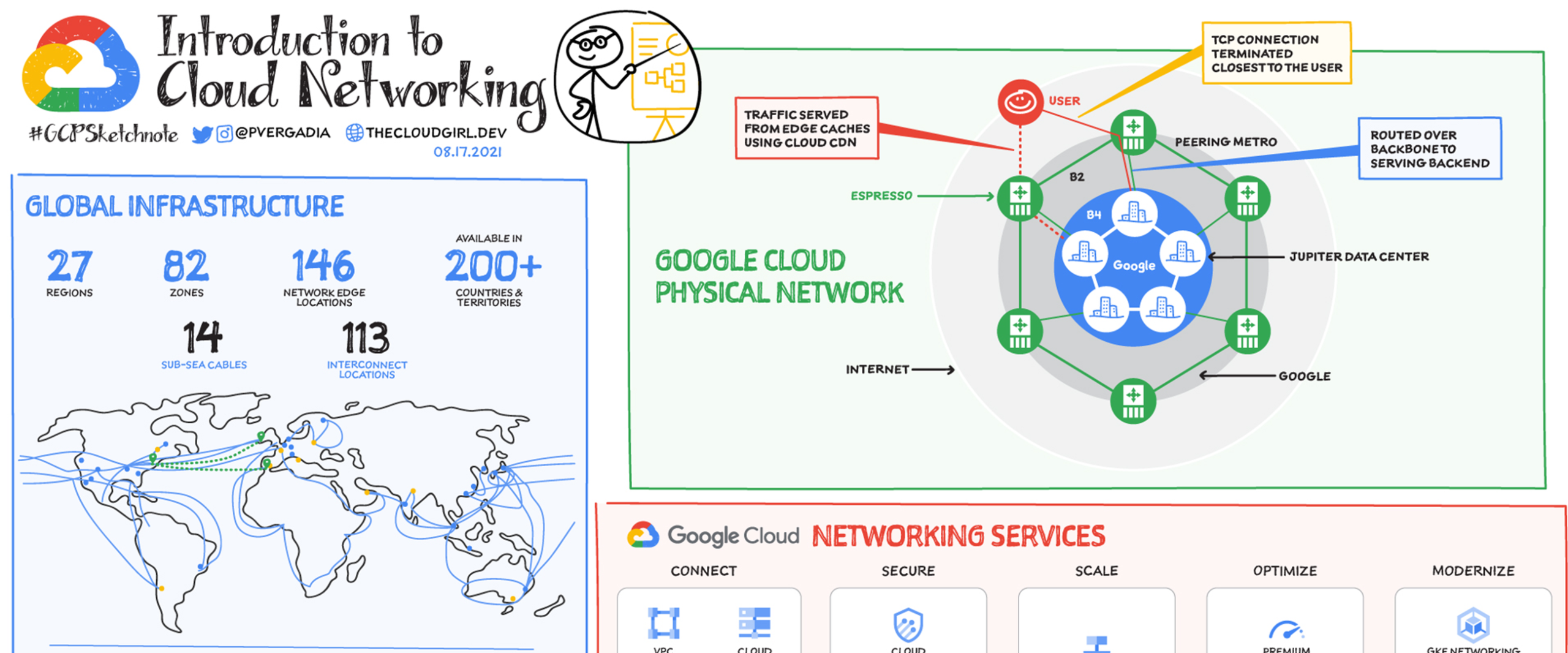
6. Networking & VPC Integration
Cloud SQL provides secure connectivity options including Private IP, VPC peering, and Private Service Connect.
6.1 Private IP Connectivity
This is the most secure way to access Cloud SQL. Traffic remains internal to the VPC, no public exposure occurs.
6.2 VPC Firewall Rules
Access is controlled using granular firewall policies based on source subnet or tag.
6.3 Hybrid Connectivity
On-premises connectivity supported via:
- Cloud VPN
- Cloud Interconnect
- Partner Interconnect
Key Points Summary
- No public IP needed
- Secure hybrid connectivity supported
- Works with GKE workloads natively
FAQs
Q: Is Private Service Connect recommended for multi-tenancy?
Yes. PSC provides private consumers endpoints in large enterprises.
7. Security & Compliance
Fully Managed Relational Database Cloud SQL offers strong built-in security including encryption, IAM integration, audit logging, and compliance with major frameworks.
Security Layers
- Encryption at rest and in transit
- IAM-based authentication and authorization
- Database user credential management
- Private IP and network isolation
- Firewall-controlled access
- Cloud Audit Logs (Admin, Data Access, System Events)
Supported Compliance Standards
- SOC 1/2/3
- HIPAA
- ISO 27001 / 27017 / 27018
- GDPR
- PCI DSS
Key Points Summary
- Data encrypted automatically
- Identity-based access management
- Supports CMEK for custom key management
8. Performance Optimization
Cloud SQL provides performance diagnostics, query insights, storage auto-scaling, and advanced tuning recommendations.
8.1 Query Insights
Visual dashboard displaying:
- High latency queries
- Top slow SQL operations
- Wait events
- Query plans and optimization hints
8.2 Storage Optimization
Automatic resizing prevents storage-related downtime and throughput bottlenecks.
8.3 SQL Tuning Best Practices
- Normalize data structure and avoid unnecessary joins
- Add appropriate indexes for WHERE and JOIN conditions
- Avoid SELECT *
- Use query plans for tuning
- Partition large tables
Key Points Summary
- Monitor CPU, RAM, IOPS in real time
- Use read replicas for analytical workloads
- Use optimized machine types based on workload
9. Replication Options
Replication improves availability and read performance while enabling cross-region DR.
9.1 Types of Replication
- Read Replicas
- Cross-Region Replication
- Asynchronous Replication
- Semisynchronous Replication (MySQL)
Replication Internals
Primary (writes) --> Secondary regions (read replicas)
replicate logs asynchronously
Key Points Summary
- Great for global distribution
- Offload analytical workloads
- Disaster recovery setup within minutes
10. Migration Strategies to Fully Managed Relational Database Cloud SQL
Cloud SQL supports seamless migration from on-premise or cloud-hosted databases using Google Database Migration Service.
Supported Migration Types
- Homogeneous: MySQL → MySQL, PostgreSQL → PostgreSQL, SQL Server → SQL Server
- Heterogeneous: Using dump and restore or third-party tools
Zero-Downtime Migration Using DMS
DMS captures ongoing changes using log-based CDC and synchronizes source and target databases.
Key Points Summary
- Near-zero downtime during cutover
- Automatic conflict detection
- Built-in health checks for source and target
FAQs
Q: How long does DMS migration take?
Depends on database size, network speed, and CDC rate.
11. Troubleshooting Guide with Scripts (PowerShell, gcloud, SQL, API)
This section provides a full set of real-world troubleshooting scripts for Fully Managed Relational Database Cloud SQL.
11.1 PowerShell Scripts (SQL Server)
11.2 gcloud Commands
11.3 SQL Queries for Troubleshooting
11.4 API-Based Troubleshooting
Key Points Summary
- Use Query Insights for deep performance issues
- Check firewall rules if connection fails
- Monitor storage capacity and auto-scaling
12. Cost Optimization Techniques
Cloud SQL allows enterprises to control spending while maintaining strong performance.
12.1 Committed Use Discounts (CUDs)
Save up to 50% by committing to 1 or 3-year capacity.
12.2 Right-Sizing Instances
Use Query Insights to identify underutilized databases.
12.3 Read Replicas for Workload Separation
Run heavy reporting on replicas instead of primary compute nodes.
Key Points Summary
- Enable storage auto-resize
- Purchase committed use discounts
- Separate workloads for cost efficiency
13. Common Enterprise Use Cases
- E-commerce & order processing systems
- SaaS application backends
- Financial platforms and high-volume transactions
- ERP, CRM, and inventory management
- Analytics and reporting infrastructure
- Healthcare and regulated workloads
- Microservices architecture supporting multiple services
Key Points Summary
- Cloud SQL supports scaling from startups to large enterprises
- Secure, compliant, and highly available
- Suitable for cross-region and global distribution
14. Internal & External References
Internal Resources:
External DoFollow References:
15. Conclusion
Fully Managed Relational Database Cloud SQL has transformed how enterprises deploy and manage relational workloads. From automated backups and HA to intelligent performance tuning, global replication, and integrated security, Cloud SQL delivers unmatched reliability and operational simplicity.
Whether you are running MySQL, PostgreSQL, or SQL Server workloads, Cloud SQL helps reduce operational overhead, increase agility, and achieve compliance, making it a top choice for modern cloud-driven organizations.
With strong integration across Google Cloud services, it enables businesses to adopt scalable, global-ready architectures that support mission-critical applications.





注册免费账户
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?