Let’s dive deeply into real-world examples and scenarios
of how Enterprise Application SSO is configured using SAML, OAuth
2.0, and OpenID Connect (OIDC). Each protocol has different use
cases, flows, and configurations. I’ll walk you through complete setups and
detailed end-to-end scenarios for each one.
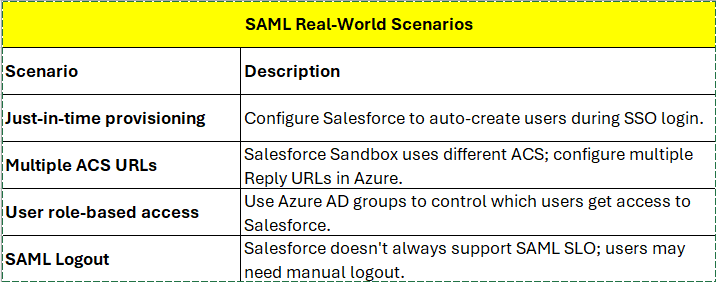
1. SAML SSO — Example: Azure AD + Salesforce
Scenario
You’re an IT admin for a company that uses Salesforce as its
CRM. You want users to log in to Salesforce using their Microsoft Entra ID
(Azure AD) credentials, with SAML-based SSO.
Step-by-Step Configuration
Step 1: Create Enterprise Application in Azure AD
- Go
to Microsoft Entra Admin Center.
- Enterprise
applications > + New application.
- Search
and select Salesforce (or choose non-gallery if custom).
- Give
it a name like Salesforce-SSO and create.
Step 2: Configure SAML SSO
- Go
to the new app > Single Sign-On > Choose SAML.
- Basic
SAML Configuration:
- Identifier
(Entity ID): https://login.salesforce.com
- Reply
URL (ACS): https://login.salesforce.com?so=ORG_ID
- Sign-on
URL: (optional) https://login.salesforce.com
Step 3: Configure Attributes & Claims
- Default
claims:
- NameID:
user.userprincipalname
- email:
user.mail
- You
can customize or add group claims if needed.
Step 4: Download Metadata
- Download
the Federation Metadata XML.
Step 5: Configure Salesforce (SP Side)
- Login
to Salesforce as admin.
- Go
to Setup > Identity > Single Sign-On Settings.
- Upload
Azure AD metadata or manually fill:
- Issuer:
Azure AD Identifier
- ACS
URL: From Azure setup
- X.509
Cert: From metadata XML
Step 6: Test SSO
- Go
back to Azure and use the Test button.
- Successful
login redirects to Salesforce without prompting for credentials (if
already logged in to Azure AD).
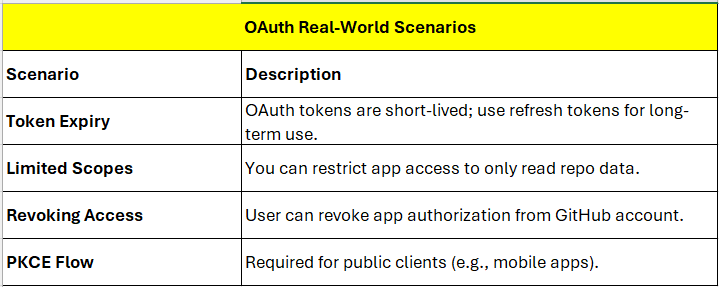
2. OAuth 2.0 — Example: GitHub Authorization via Azure AD
Scenario
You’re building a web-based internal tool that integrates
with GitHub. You want the app to allow users to log in and fetch GitHub
repositories without storing their credentials — using OAuth 2.0.
OAuth Roles
- Resource
Owner: User who owns GitHub account.
- Client:
Internal web app.
- Authorization
Server: GitHub OAuth.
- Resource
Server: GitHub APIs.
Step-by-Step OAuth Flow
Step 1: Register App in GitHub (Authorization Server)
- Go
to GitHub > Settings > Developer Settings > OAuth Apps > New
OAuth App
- App
name: Internal-GitHub-Tool
- Homepage:
https://internalapp.example.com
- Callback
URL: https://internalapp.example.com/oauth/callback
Step 2: Get Client ID and Secret
- GitHub
gives you:
- Client
ID
- Client
Secret
Step 3: Implement Authorization Code Flow in Your App
Step 3.1: Redirect to GitHub Authorization URL:
https://github.com/login/oauth/authorize?
client_id=XXXX&redirect_uri=https://internalapp.example.com/oauth/callback&scope=repo,user
Step 3.2: User logs in → GitHub sends code to redirect
URI:
https://internalapp.example.com/oauth/callback?code=AUTH_CODE
Step 3.3: Your App Exchanges Code for Access Token
POST to:
https://github.com/login/oauth/access_token
Body:
{
“client_id”: “XXXX”,
“client_secret”: “YYYY”,
“code”: “AUTH_CODE”
}
Step 3.4: GitHub Returns Access Token
{
“access_token”:
“abcdef123456…”,
“token_type”: “bearer”,
“scope”: “repo,user”
}
Step 3.5: Use Access Token to Call GitHub API
GET
https://api.github.com/user
Authorization: Bearer abcdef123456…
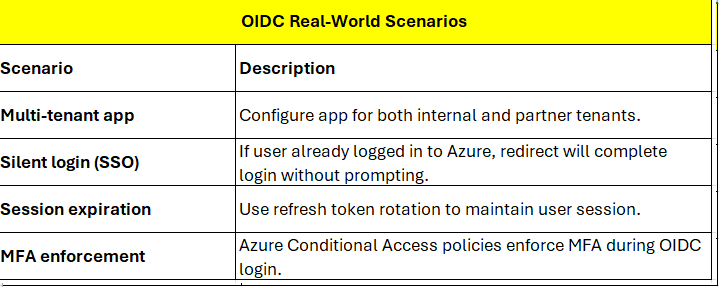
3. OpenID Connect (OIDC) — Example: Custom Web App + Azure AD Login
Scenario
You’re building a modern web app (e.g., HR Portal), and you
want users to sign in using their company Azure AD credentials. You’ll use OIDC
for both authentication and basic profile information.
Step-by-Step OIDC Setup
Step 1: Register the App in Azure AD
- Go
to App registrations > + New registration
- Name:
HR-Portal-App
- Redirect
URI: https://hr.example.com/auth/callback
- Supported
account type: Single tenant or multi-tenant.
Step 2: Configure OIDC Scopes
- Go
to API permissions > Add > Microsoft Graph:
- openid
- email
- profile
Step 3: Generate Client Secret
- Go
to Certificates & secrets > New client secret
Step 4: Discover OIDC Metadata
From:
https://login.microsoftonline.com/<tenant-id>/v2.0/.well-known/openid-configuration
You’ll find:
- Authorization
Endpoint
- Token
Endpoint
- UserInfo
Endpoint
- JWKS
URI
- Issuer
Step 5: Implement OIDC Flow
Step 5.1: Redirect
to Authorization Endpoint
https://login.microsoftonline.com/<tenant>/oauth2/v2.0/authorize?
client_id=XXXX&response_type=code&scope=openid
profile email&
redirect_uri=https://hr.example.com/auth/callback
Step 5.2: Azure
Returns Code
https://login.microsoftonline.com/<tenant>/oauth2/v2.0/token
Your app receives:
https://hr.example.com/auth/callback?code=AUTH_CODE
Step 5.3: Exchange Code for Tokens
POST to token endpoint:
Returns:
- id_token:
user identity (JWT)
- access_token:
call Microsoft Graph
Step 5.4: Decode ID Token
ID token is a JWT containing:
{
“sub”:
“abc123”,
“email”:
“john.doe@company.com”,
“name”:
“John Doe”,
“preferred_username”: “john.doe”
}
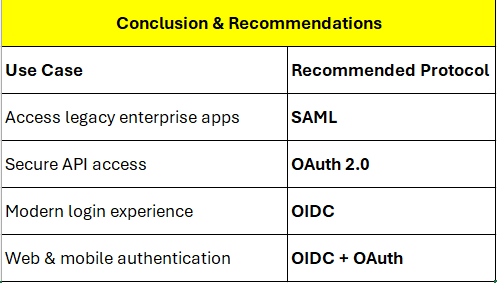
Conclusion
Implementing Single Sign-On (SSO) for enterprise
applications enhances both security and user experience by
streamlining authentication across systems. Whether you choose SAML, OAuth
2.0, or OpenID Connect (OIDC) depends on your application type,
security requirements, and integration goals.
- Use SAML
for traditional enterprise apps requiring identity federation (like
Salesforce or SAP).
- Use OAuth
2.0 when authorizing access to APIs without exposing credentials.
- Use OIDC
for modern applications needing identity verification and user profile
access.
By following the detailed configurations and real-world
scenarios provided, you can confidently implement secure and scalable SSO for
your enterprise needs.
SSO is no longer just a convenience—it’s a critical component of modern identity and access management (IAM) strategies. Leveraging Microsoft Entra ID or other IdPs with these protocols ensures compliance, control, and seamless user access across your digital ecosystem.
Update (July 2025)
Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure Active Directory)
continues to enhance its support for modern identity protocols with
improved tooling, conditional access integration, and multi-cloud SSO support.
- OIDC
& OAuth 2.0 are now the preferred standards for most new
applications, especially for hybrid cloud environments.
- Microsoft
recommends using OIDC over SAML for custom app development to
leverage modern identity tokens and scalable APIs.
Stay tuned for upcoming tutorials where we’ll explore SSO
with REST APIs, Conditional Access, and multi-tenant configurations using
Microsoft Entra External ID and Entra Verified ID.












Leave a Reply