Introduction to AWS Lambda
In today’s cloud-first world, automation and scalability are key. AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service from Amazon Web Services (AWS) that lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. It’s designed to automatically scale your applications based on demand while optimizing cost and performance.
Whether you’re building microservices, automating workflows, or integrating third-party APIs, AWS Lambda offers a fast, flexible, and cost-effective approach to modern application development.
Learn more about AWS Services and Serverless Architecture on CloudKnowledge.in.

How AWS Lambda Works
At its core, AWS Lambda executes code in response to events. You simply upload your code, set up triggers, and AWS handles the rest — provisioning, scaling, monitoring, and logging.
How to Use AWS Lambda: Step-by-Step
Write your function in one of the supported languages (Node.js, Python, Java, Go, etc.).
Upload or deploy it directly via the AWS Console, CLI, or CI/CD pipelines.
Set up event sources, such as:
S3 bucket events (e.g., file upload)
DynamoDB stream updates
API Gateway requests
CloudWatch alarms or scheduled events
AWS Lambda executes your code automatically when triggered.
Pay only for compute time — no idle server cost.
Check out our detailed AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) Guide to learn how to securely manage Lambda permissions.
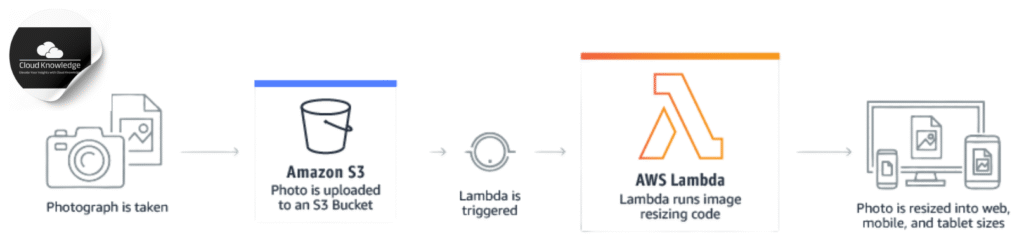
Types of AWS Lambda Functions
AWS Lambda supports multiple execution models and use cases. Below are the main types of Lambda functions based on how they’re invoked or integrated:
-
Event-driven Functions – Triggered by AWS services like S3, DynamoDB, or SNS.
-
HTTP API-based Functions – Integrated with API Gateway for RESTful APIs.
-
Stream-based Functions – Used for real-time data processing from Kinesis or Kafka.
-
Scheduled (Cron) Functions – Triggered using CloudWatch rules at specific times.
-
Manual Invocation Functions – Run manually through AWS Console or SDK for testing or one-time jobs.
Combinations and Integrations with AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda’s power lies in its integrations. It works seamlessly with other AWS services to create automated workflows and event-driven architectures.
Here are some powerful combinations:
Lambda + S3: Automate file processing, image resizing, or log parsing.
Lambda + API Gateway: Build serverless APIs and web backends.
Lambda + DynamoDB: React to real-time database changes.
Lambda + Step Functions: Create orchestrated workflows across multiple services.
Lambda + CloudWatch: Monitor events and trigger alerts automatically.
Lambda + SNS/SQS: Enable asynchronous message-based communication between services.
Explore more AWS automation guides at CloudKnowledge.in.
Advantages of AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda offers several benefits that make it a go-to choice for developers and businesses:
-
Serverless Architecture: No infrastructure management — AWS handles everything.
-
Automatic Scaling: Scales based on incoming events or load automatically.
-
Cost Efficiency: Pay only for the time your code runs (per millisecond).
-
High Availability: Runs across multiple AWS Availability Zones.
-
Flexible Language Support: Supports Python, Node.js, Java, C#, Go, and Ruby.
-
Integration Ready: Easily integrates with AWS and third-party services.
-
Security & IAM: Fine-grained permissions via AWS IAM roles.
Disadvantages of AWS Lambda
While Lambda is powerful, it also comes with certain limitations that need to be considered:
Cold Start Delays: First-time function invocation may have latency.
Execution Time Limit: Maximum runtime is 15 minutes.
Limited Temporary Storage: Only 512 MB of
/tmpstorage available.Complex Debugging: Troubleshooting distributed, event-driven systems can be difficult.
Vendor Lock-In: Heavily tied to AWS infrastructure and ecosystem.
Limited Concurrency by Default: Default limit of 1,000 concurrent executions (can be increased).
Want to compare Lambda with Azure Functions or Google Cloud Functions? Read our Multi-Cloud Serverless Comparison.
Best Practices for AWS Lambda (2025 Update)
To get the most out of AWS Lambda, follow these latest best practices:
-
Use Environment Variables for configuration and secrets.
-
Keep Functions Lightweight – minimize dependencies.
-
Implement Error Handling with retries and dead-letter queues (DLQs).
-
Monitor Metrics via AWS CloudWatch.
-
Use Layers to share common code or libraries.
-
Secure IAM Roles – assign the least privilege possible.
-
Leverage CI/CD Pipelines using AWS CodePipeline and CodeDeploy for automation.
Real-World Use Cases of AWS Lambda
Here are some practical examples where AWS Lambda adds value:
-
Automated Data Backups: Triggered when a file is uploaded to S3.
-
Real-Time Image Processing: Resize or watermark images dynamically.
-
IoT Device Integration: Process sensor data from IoT Core.
-
Chatbot Backends: Handle events and responses via API Gateway.
-
Log Processing Pipelines: Analyze CloudTrail or application logs in real time.
Pricing Model
AWS Lambda pricing is based on requests and compute time.
-
Free tier: 1 million requests and 400,000 GB-seconds per month.
-
Beyond that: Charged per request and per millisecond of execution time.
For cost optimization tips, visit AWS Cost Management Guide.
Additional Information: Monitoring and Security
AWS provides CloudWatch and X-Ray for performance monitoring and tracing.
For enhanced security:
Use AWS KMS for encryption.
Implement VPC integration for private subnet access.
Enforce IAM least privilege principles for Lambda roles.
For more, read our guide on AWS Security Best Practices.
Conclusion
AWS Lambda continues to revolutionize how developers build and scale modern applications. With its serverless architecture, automatic scaling, and pay-per-use model, Lambda is ideal for automation, microservices, and event-driven solutions.
While there are limitations like cold starts and execution timeouts, the benefits far outweigh the trade-offs — especially when combined with other AWS services.
As cloud computing evolves, mastering AWS Lambda is an essential step for any cloud engineer or developer looking to build scalable, efficient, and future-ready solutions.
Explore more in-depth cloud tutorials and AWS articles on CloudKnowledge.in.
Top SEO Keywords for Ranking
AWS Lambda, serverless compute, AWS automation, AWS functions, Lambda use cases, AWS serverless examples, Lambda vs EC2, AWS Lambda advantages and disadvantages, AWS integration, serverless deployment





Leave a Reply