Azure provides two key options for hosting static websites: Azure Storage static website hosting and Azure Static Web Apps. Both options are serverless and suitable for scenarios where dynamic server-side rendering is not required. Here’s a breakdown:
Azure Storage Static Website Hosting
- Purpose: For serving static files (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images) directly from an Azure Storage container.
- Key Features:
- No server-side rendering.
- Low cost and simple setup.
- Ideal for basic static sites or serving assets like images and documents.
- Limitations:
- No support for authentication (AuthN) or authorization (AuthZ).
- No custom header configuration (requires Azure CDN for advanced features).
- No integrated CI/CD workflows.
Azure Static Web Apps
- Purpose: A more feature-rich option for static site hosting with integrated modern development workflows.
- Key Features:
- Fully managed CI/CD from GitHub or Azure DevOps repositories.
- Built-in support for custom headers.
- Support for authentication and authorization (AuthN/AuthZ).
- Free SSL certificates and automatic HTTPS.
- Global scale with content served from multiple points of presence.
- Integration with Azure Functions for serverless APIs.
- Use Cases:
- More complex static websites or SPA frameworks (React, Angular, Vue).
- Projects requiring user authentication, dynamic routing, or custom headers.
Steps to Set Up Static Website Hosting in Azure Storage
1. Enable Static Website Hosting
- Go to the Azure Portal and navigate to your Storage Account.
- In the left-hand menu, under Data Management, click Static website.
- Click Enable to turn on static website hosting.
- Specify:
- Index document name: The default file (e.g.,
index.html). - Error document path (optional): Path to a custom 404 page (e.g.,
404.html).
- Index document name: The default file (e.g.,
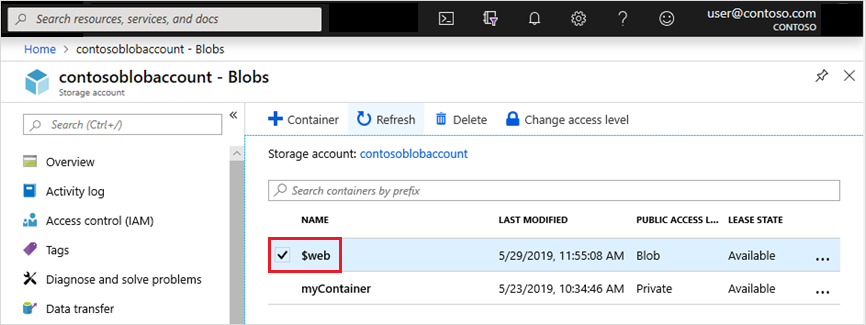
2. Create the $web Container
- If not already created, enabling static website hosting will automatically create a special container named
$webin your storage account. - This container is where you’ll upload your website’s files.
3. Upload Your Website Files
- Go to the Containers section of the storage account in the Azure Portal.
- Select the
$webcontainer. - Click Upload to add your site’s static files (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images, etc.).
4. Access Your Static Website
- After enabling the feature, Azure generates a primary endpoint URL for your static website (e.g.,
https://<storage_account_name>.z26.web.core.windows.net). - Copy the URL from the Static website pane in the portal.
- Navigate to the URL in a browser to view your website.
Additional Notes
- Custom Domain: If you want to use a custom domain instead of the default endpoint, configure a custom domain in the Azure Portal.
- Azure CDN: For custom headers, caching, or improving performance with global delivery, integrate Azure Content Delivery Network (CDN) with your storage account.
- Permissions: Ensure that the files in the
$webcontainer have public read access for them to be accessible as part of the static website.
Viewing Website Content
- Public URL:
- The public URL of the website is accessible through the Azure portal, Azure CLI, or PowerShell.
- Example:
https://<storage_account_name>.z22.web.core.windows.net
- Index Document:
- The default document (e.g.,
index.html) loads when users navigate to the root URL without specifying a file.
- The default document (e.g.,
- 404 Error Handling:
- If no custom 404 page is specified, Azure returns a default error page.
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS)
- Unsupported: Static website hosting does not support CORS configurations directly.
- If CORS is critical, consider using Azure CDN or other services to handle CORS.
Secondary Endpoints
- Redundancy:
- For accounts configured with geo-redundancy, secondary endpoints are accessible.
- Example:
https://<storage_account_name>-secondary.z22.web.core.windows.net. - Caveat: Secondary data is replicated asynchronously, so content may not be fully in sync with the primary endpoint.
Access Level and Permissions
- $web Container Access:
- Modifying access level (e.g., private or blob-level access) affects only the blob service endpoint (
https://<storage_account_name>.blob.core.windows.net/$web/index.html), not the static website endpoint. - The static website endpoint always uses anonymous access.
- Modifying access level (e.g., private or blob-level access) affects only the blob service endpoint (
- Storage Account Permissions:
- Enabling static website hosting requires either:
Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/writepermission, or- A shared key.
- Built-in role: Storage Account Contributor.
- Enabling static website hosting requires either:
Custom Domains
- HTTP and HTTPS:
- HTTP: Supported natively with custom domains.
- HTTPS: Requires Azure CDN for custom domain HTTPS support.
- Secure transfer over HTTPS is enforced if the storage account is configured for secure transfer.
- Azure DNS:
- Hosting the domain on Azure DNS simplifies management.
Headers and Caching
- Adding Headers:
- Static website hosting doesn’t allow header configurations directly.
- Use Azure CDN to add or modify headers, including caching headers.
- Caching:
- Control caching behavior with Azure CDN caching rules.
Multi-Region Hosting
- Use Azure Front Door for multi-region hosting, as it supports:
- Different content per region.
- Failover capabilities.
- Avoid Azure Traffic Manager with custom domains, as it may cause domain verification issues.
Metrics and Pricing
- Metrics:
- Enable metrics to track website traffic and performance through the
$webcontainer.
- Enable metrics to track website traffic and performance through the
- Pricing:
- Static website hosting itself is free.
- Charges apply for:
- Blob storage space.
- Operations (e.g., reads/writes).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Does the Azure Storage firewall work with a static website?
- Yes. The Azure Storage firewall supports static website endpoints.
- You can use IP-based and VNET firewall rules to secure your static website.
2. Do static websites support Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD)?
- No. Static websites only support anonymous read access for files in the
$webcontainer.
3. How do I use a custom domain with a static website?
- You can configure a custom domain with a static website using Azure Content Delivery Network (Azure CDN).
- Azure CDN enhances performance and provides low-latency access globally.
4. How do I use a custom Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate with a static website?
- To use a custom SSL certificate:
- Configure it through Azure CDN.
- Azure CDN ensures consistent performance and secure HTTPS connections for your custom domain.
5. How do I add custom headers and rules with a static website?
- Use the Azure CDN Rules Engine to:
- Configure custom headers.
- Apply custom rules (e.g., caching, redirects).
- Feedback on this functionality is welcomed by Azure.
6. Why am I getting an HTTP 404 error from a static website?
- Common causes of 404 errors:
- Case-sensitivity: URLs and file names are case-sensitive. For example,
Index.htmlwon’t work if the actual file is namedindex.html. - Azure CDN propagation delay: If using Azure CDN, allow up to 90 minutes for the endpoint provisioning to propagate globally.
- Case-sensitivity: URLs and file names are case-sensitive. For example,
7. Why isn’t the root directory of the website redirecting to the default index page?
- Verify the configuration in the Azure portal:
- Go to the Static website configuration page of your storage account.
- Check the Index document name field and ensure it matches the file name (including case) in the
$webcontainer.
- File names and extensions are case-sensitive.










The Knowledgeable and Latest way of Duplicate Attribute Resiliency - Cloud Knowledge
[…] Attribute Resiliency in Microsoft Entra ID addresses conflicts caused by duplicate UserPrincipalName (UPN) and SMTP ProxyAddress attributes during synchronization. These attributes must remain unique […]